
#MICROSOFT REMOTE DESKTOP MANAGER WINDOWS 10 INSTALL#
RDS PowerShell is installed when you install the Remote Desktop services role. Step 1: Install Remote Desktop services role To get started, first install the Remote Desktop services role and then launch RDS PowerShell. You view, navigate and work with RDS provider as you would with any of the other providers.
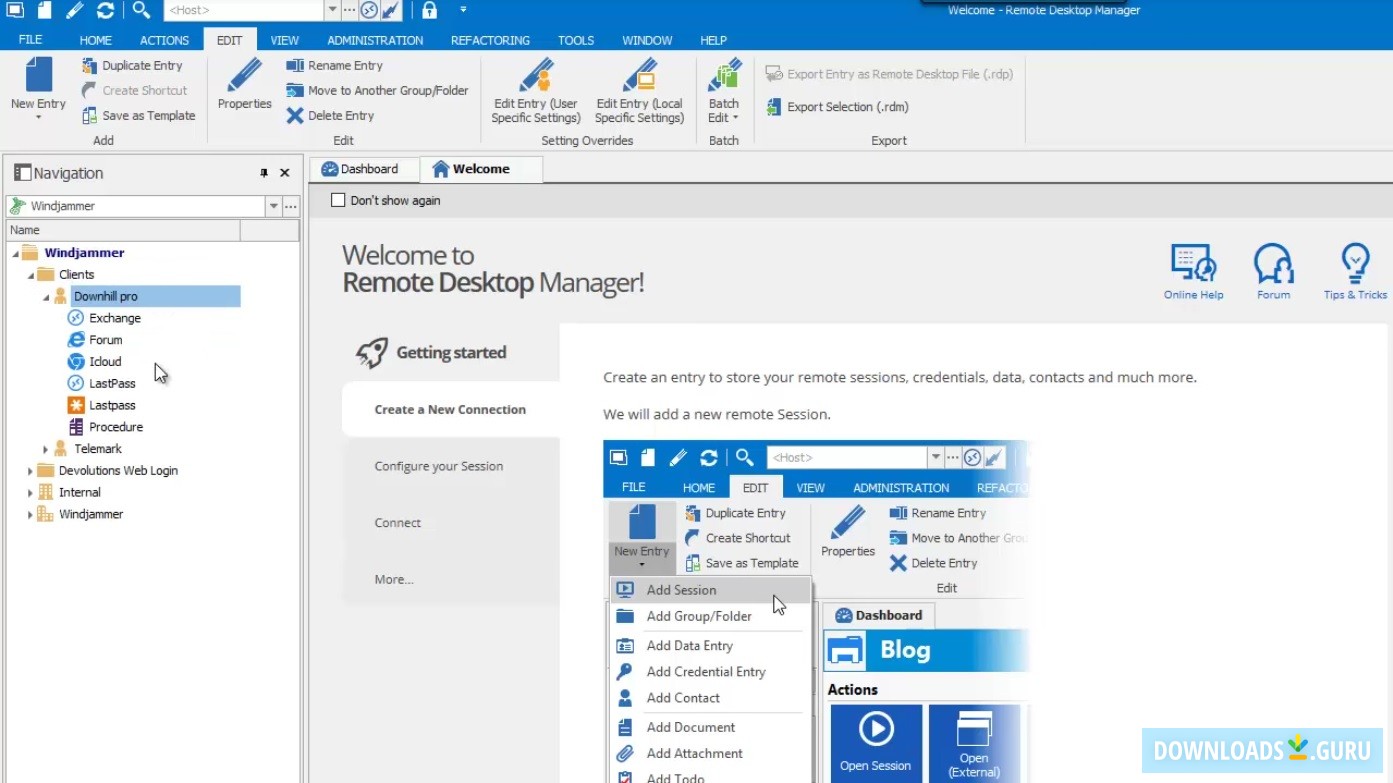
Think of RDS Provider as something similar to file system provider and registry provider, IIS Provider. This Provider (we’ll call it RDS provider in the rest of this post) allows you to view and manage the configuration of all role services and components of Remote Desktop Services. Once you install the Remote Desktop services role, a PowerShell provider gets installed. Read further to understand RDS PowerShell in detail. As always, we are eager to hear what you think and it is important that you let us know what you like and don’t like as early as possible. Install the beta release of Windows Server 2008 R2 and give this feature a try. Of course there is a lot more that you can do with Windows PowerShell. Create and manage Gateway Resource Access & Client Access policies Configure and assign virtual IP addresses to either sessions or applicationsħ. Create and configure a Remote Desktop server farmĥ. View and edit configuration settings of Remote Desktop serverĤ. For example, below are few management tasks that you can now do with PowerShellġ.

You can now configure and manage all RDS role services and components using PowerShell. We are pleased to announce that the Beta release of Windows server 2008 R2 supports managing Remote Desktop services using PowerShell.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
